

But there’s a lot you can do to reduce the chances of it happening. Because of this, you might not notice any problem until there’s significant blockage or even a heart attack. Catch CAD before it gets worseĬAD often develops over time. This involves inserting a thin and flexible tube or injecting a dye into the coronary arteries. Helps determine if there’s blockage in your arteries. Helps determine your heart’s condition when it’s under stress.ĭevelops a picture of your heart, lungs and other organs using X-rays. Uses ultrasound to develop a picture of your heart. Measures your heart rate, electrical activity, and the regularity of your heartbeat. If your doctor suspects CAD, they may advise you to take one or more of the following tests: Your doctor will diagnose CAD based on your family and medical history, risk factors, physical exam, and results from other tests.ĬAD cannot be diagnosed by a single test.

Sometimes, heart attacks may occur without any apparent warning signs. Women may experience less obvious signs such as pain in the neck or jaw. Signs of an impending heart attack include extreme pressure in the chest, pain in the shoulder or arm, and sometimes sweating and shortness of breath. Heart attack: When a coronary artery is completely blocked a heart attack may result.
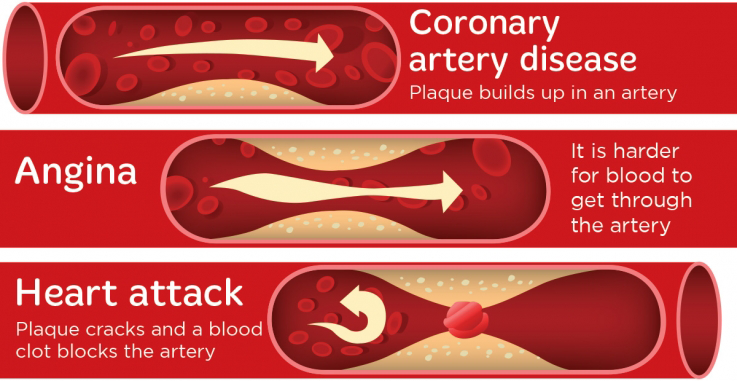 Shortness of breath: Because the heart isn’t pumping enough blood for your body’s needs, you may experience shortness of breath or fatigue. After stopping the stress-inducing activity, you’ll feel the pain go away. This pain is also known as angina and is typically triggered by emotional or physical stress. Chest pain: You feel a lot of pressure or tightness in the middle or on the left side of your chest. But when there’s significant plaque buildup, you may experience the following symptoms. When your coronary arteries are narrowed, it’s difficult to supply enough nourishment to the heart, especially when exercising.Īt first, the decrease in the amount of oxygen, blood, and nutrients to the heart may not be noticeable. By taking the necessary steps and adjustments, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing CAD. Ongoing research seeks to identify other possible risk factors such as sleep apnea, high triglycerides, homocysteine, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). Other risk factors include obesity, high stress levels, and insufficient physical activity. Diabetes is generally associated with an increased risk of CAD. A low level of High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), or good cholesterol, suggests atherosclerosis. This increase in cholesterol levels may result from a high level of Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), also referred to as bad cholesterol. High cholesterol levels: A high level of cholesterol in the blood increases the risk of plaque and atherosclerosis. High blood pressure: When not controlled, high blood pressure may cause the coronary arteries to harden and grow thicker, ultimately constricting them. Smoking: Both smoking and secondhand smoke increases the risk of developing CAD. If your brother or father was diagnosed with heart disease before the age of 55 or your sister or mother gets the same diagnosis before the age of 65, you have a high risk of developing CAD. Family history: Families with a history of heart disease are considered to be at a higher risk. Gender: Generally, the risk for CAD is higher in men than in women, whose risk increases after menopause. The older you get, the higher the chances that your coronary arteries are narrowing and becoming damaged. Age: The buildup of plaque begins in childhood and deposits grow over time. What are the risk factors for Coronary Artery Disease? A complete blockage of the artery may even lead to a heart attack. Is CAD the same as Coronary Heart Disease?Īlthough sometimes used interchangeably, CAD and Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) aren’t the same condition. With time, limited blood flow may cause a patient to experience shortness of breath, chest pain, and other related symptoms. When plaque builds up or blood vessels swell, arteries narrow and the flow of blood to the heart is obstructed. Inflammation is also a major cause of CAD. Usually, damaged blood vessels are caused by a buildup of plaque (cholesterol-containing deposits) on artery walls. Coronary arteries are the main blood vessels that nourish the heart by supplying it with blood, oxygen, and nutrients. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a heart disease that results from the damage or infection of coronary arteries.
Shortness of breath: Because the heart isn’t pumping enough blood for your body’s needs, you may experience shortness of breath or fatigue. After stopping the stress-inducing activity, you’ll feel the pain go away. This pain is also known as angina and is typically triggered by emotional or physical stress. Chest pain: You feel a lot of pressure or tightness in the middle or on the left side of your chest. But when there’s significant plaque buildup, you may experience the following symptoms. When your coronary arteries are narrowed, it’s difficult to supply enough nourishment to the heart, especially when exercising.Īt first, the decrease in the amount of oxygen, blood, and nutrients to the heart may not be noticeable. By taking the necessary steps and adjustments, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing CAD. Ongoing research seeks to identify other possible risk factors such as sleep apnea, high triglycerides, homocysteine, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). Other risk factors include obesity, high stress levels, and insufficient physical activity. Diabetes is generally associated with an increased risk of CAD. A low level of High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), or good cholesterol, suggests atherosclerosis. This increase in cholesterol levels may result from a high level of Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), also referred to as bad cholesterol. High cholesterol levels: A high level of cholesterol in the blood increases the risk of plaque and atherosclerosis. High blood pressure: When not controlled, high blood pressure may cause the coronary arteries to harden and grow thicker, ultimately constricting them. Smoking: Both smoking and secondhand smoke increases the risk of developing CAD. If your brother or father was diagnosed with heart disease before the age of 55 or your sister or mother gets the same diagnosis before the age of 65, you have a high risk of developing CAD. Family history: Families with a history of heart disease are considered to be at a higher risk. Gender: Generally, the risk for CAD is higher in men than in women, whose risk increases after menopause. The older you get, the higher the chances that your coronary arteries are narrowing and becoming damaged. Age: The buildup of plaque begins in childhood and deposits grow over time. What are the risk factors for Coronary Artery Disease? A complete blockage of the artery may even lead to a heart attack. Is CAD the same as Coronary Heart Disease?Īlthough sometimes used interchangeably, CAD and Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) aren’t the same condition. With time, limited blood flow may cause a patient to experience shortness of breath, chest pain, and other related symptoms. When plaque builds up or blood vessels swell, arteries narrow and the flow of blood to the heart is obstructed. Inflammation is also a major cause of CAD. Usually, damaged blood vessels are caused by a buildup of plaque (cholesterol-containing deposits) on artery walls. Coronary arteries are the main blood vessels that nourish the heart by supplying it with blood, oxygen, and nutrients. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a heart disease that results from the damage or infection of coronary arteries.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
